
Behavioural changes which affect the way people use energy are an important part of the toolkit for reaching net zero emissions by 2050.

Applying behavioural science to environmental challenges can help policymakers better target and redirect unsustainable behaviours. This report draws on published work to provide an overview of behaviourally informed interventions, why they should be considered by governments and how they can be devised and applied.

For the world to reach net zero, consumers everywhere will have to make fundamental changes to how they travel, heat, cool and power their homes, the food they eat and the products they buy.

This report of the Cambridge Sustainability Commission on Scaling Sustainable Behaviour Change draws on research syntheses about the potential contributions of behaviour change towards climate and sustainability goals to attain the goals of the Paris Agreement.

Provides a foundational understanding of technical and social aspects related to online privacy
Covers modern application areas as well as underexplored issues (e.g., privacy accessibility, cross-cultural privacy)
Includes a dedicated part on forward-looking approaches to privacy that move beyond one-size-fits-all solutions.
An inside view of the experimental practices of cognitive psychology—and their influence on the addictive nature of social media

Download free Experientia report on key trends and design challenges in home and remote care when patient and caregivers use online platforms and on-body health devices

Rapporto gratuito su tendenze chiave e sfide di design nell'assistenza a domicilio e a distanza quando il paziente e i caregiver usano piattaforme online e dispositivi per la salute.

Danish social scientist Michael Bang Petersen illuminates the evolutionary foundations and social processes involved in the spread of outright falsehoods.

People care and act to manage their privacy, but face steep psychological and economic hurdles that make not just desired, but also desirable privacy nearly unattainable. Approaches to privacy management that rely purely on market forces and consumer responsibilization have failed.

The use of nudge theory to inform policy interventions in response to COVID-19 has re-opened debates over the politically paternalistic nature of governing by ‘nudges’ and has given momentum to calls to include the more participatory elements of co-design into policymaking

Several Covid-19 policies have shown "just how deeply some governments distrust their citizens. As if the virus was not enough, the public was portrayed as an additional part of the problem". But, asks Prof. Stephen Reicher of the University of St Andrews, "is this an accurate view of human behaviour"?
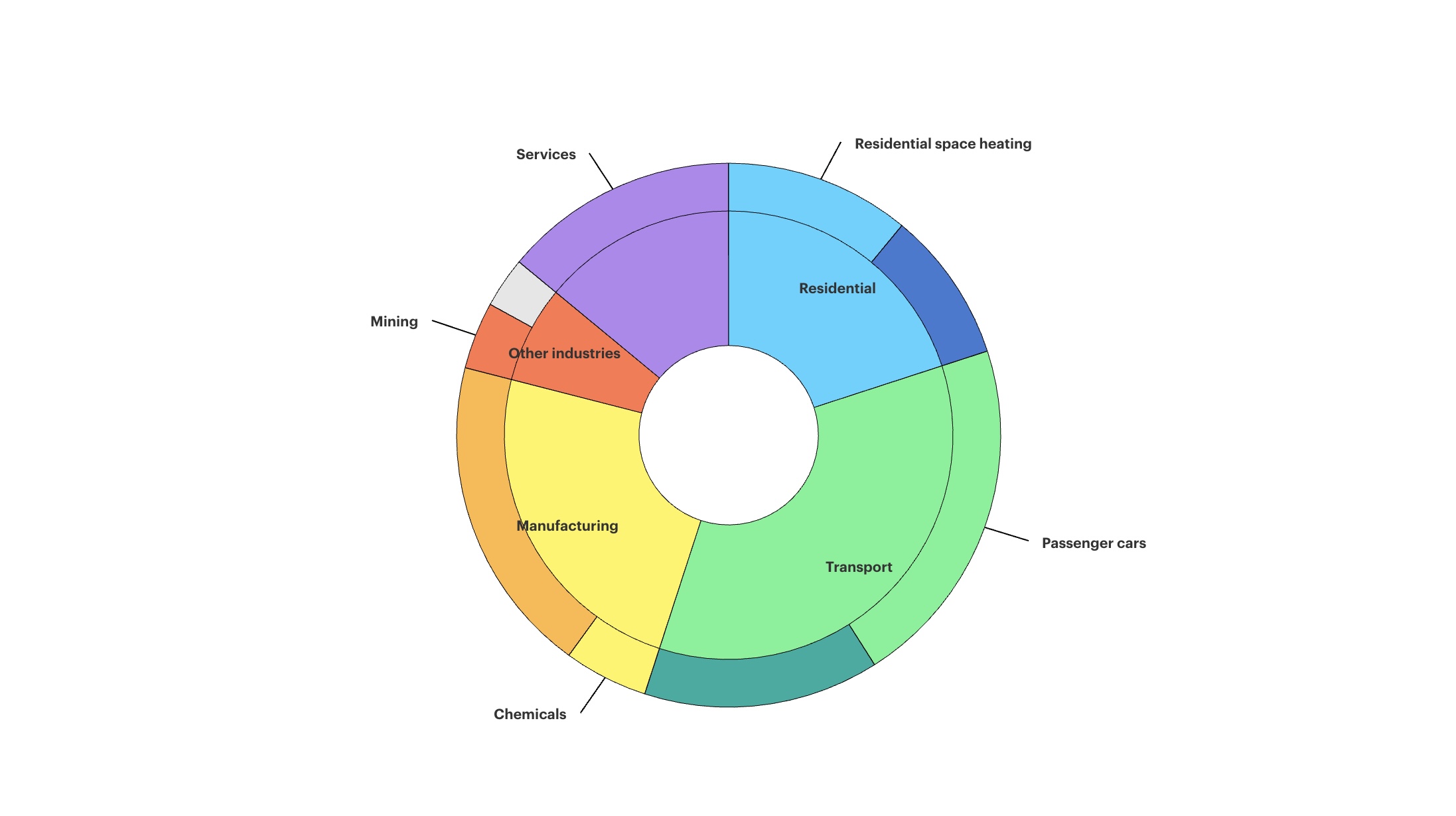
Individuals and households can adopt a variety of measures to optimise their energy consumption, writes Elisabatta Cornago of the International Energy Agency. This article focuses on the potential for enhancing energy efficiency with policies and programmes designed to educate consumers and encourage them to alter their daily habits – without resorting to large-scale structural improvements.

During its first year of activity, the Behavioural Insights Platform of the UsersTCP, with the IEA (International Energy Agency), has developed an environment scan report assessing how behavioural insights have been applied to demand-side energy policy and programmes.
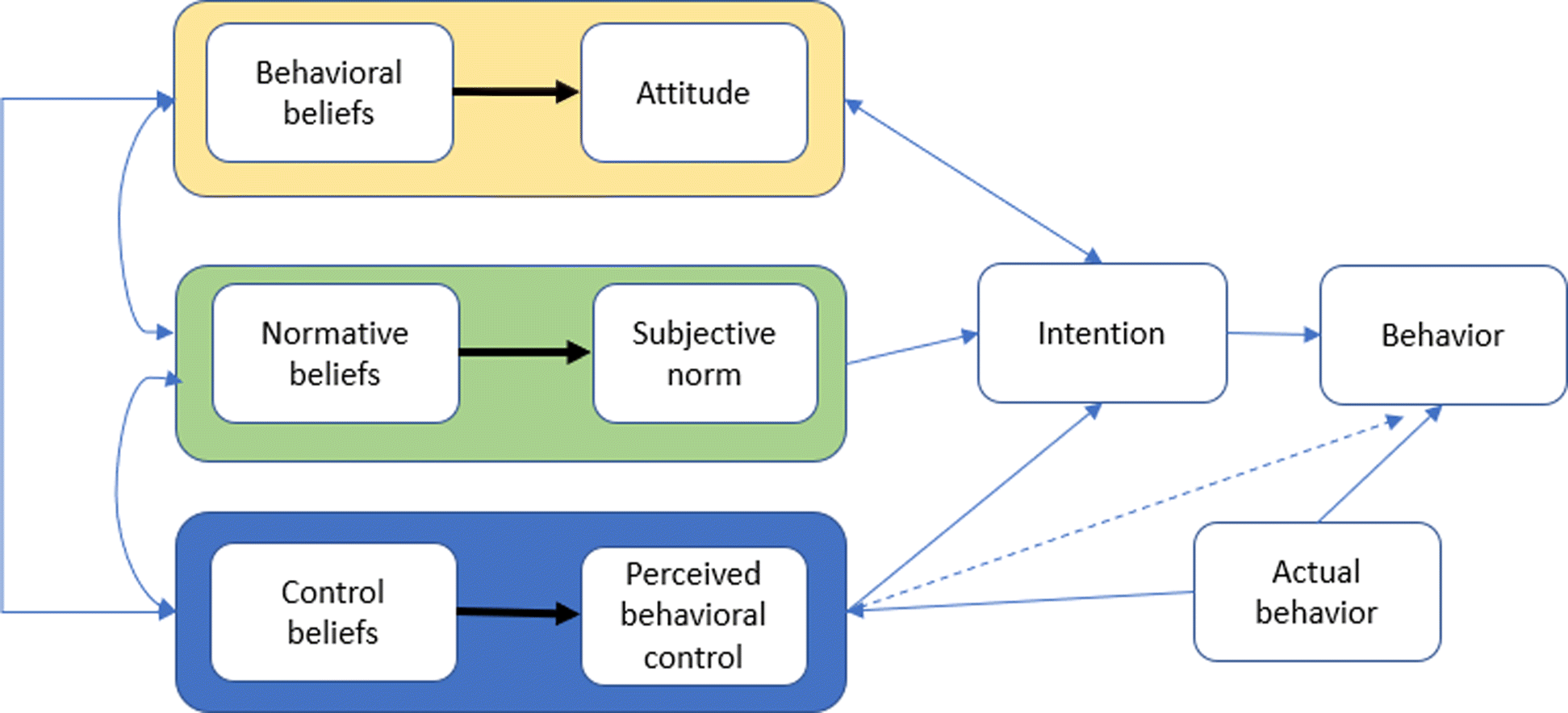
Since the majority of cyber incidents are human enabled, this shift requires expanding research to underexplored areas such as behavioral aspects of cybersecurity. This paper provides a review of relevant theories and principles, and gives insights including an interdisciplinary framework that combines behavioral cybersecurity, human factors, and modeling and simulation.

CyberBitsEtc. is a website and blog by Ganna Pogrebna (Professor of Behavioural Economics and Data Science, Fellow at the Alan Turing Institute) and Boris Taratine (Cyber Security Architect and Visionary) that focuses a lot on the human aspects of cyber security, in particular behavioural design, psychology and behavioural sciences.

In their new book, Daniel Kahneman, Olivier Sibony and Cass Sunstein offer strategies for improvement | An Economist book review

7 day online interactive course with vertical, thematic focus on tools and methods of behavioral design for cultural change to tackle societal challenges
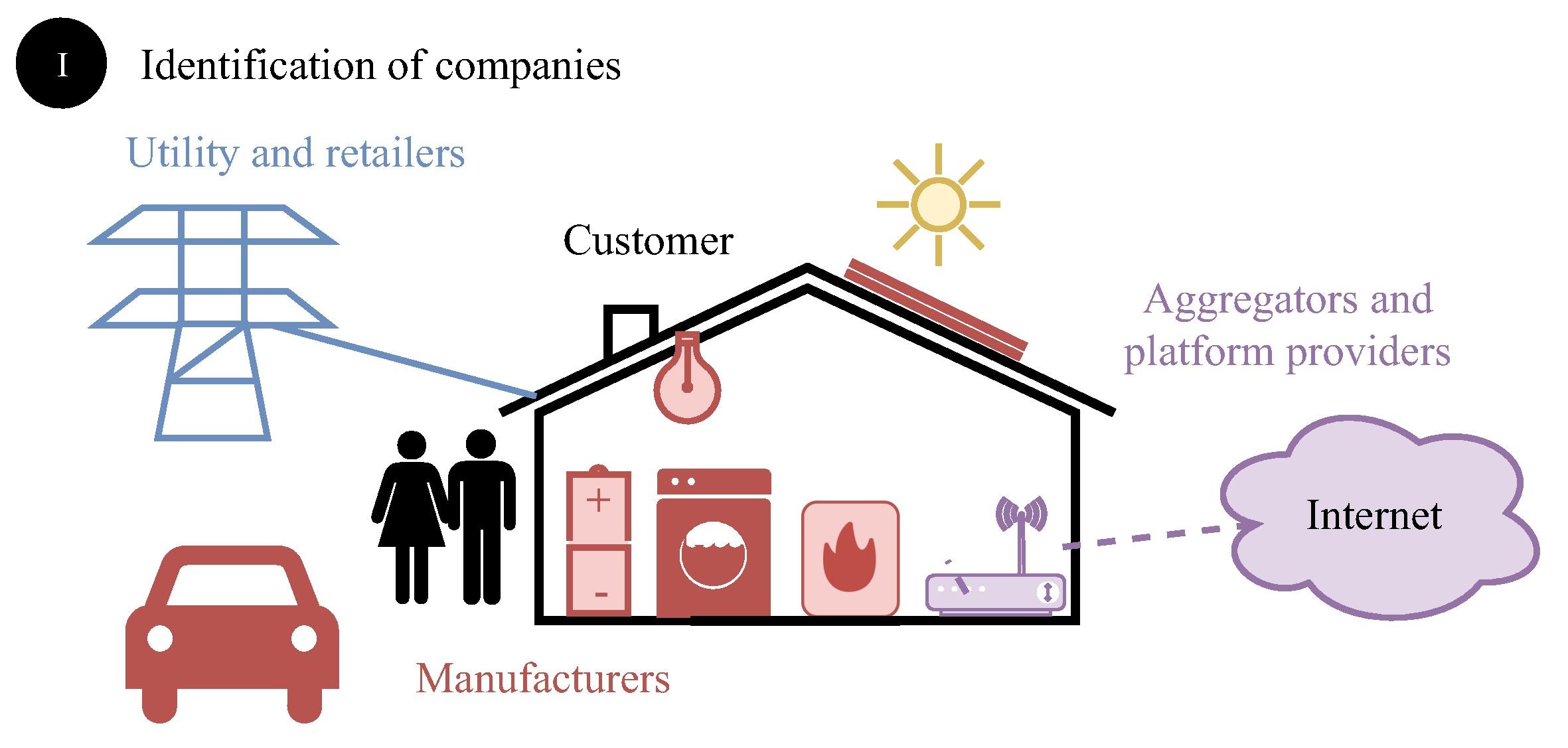
Designing energy services with a human-centered approach will allow us to rely on consumers not only as executors of changes in energy consumption, but also as providers of data.
Provocative and engaging in both its broad scope and its surprising details, The WEIRDest People in the World explores how culture, institutions, and psychology shape one another, and explains what this means for both our most personal sense of who we are as individuals and also the large-scale social, political, and economic forces that drive human history.




















